CBD oil is associated with a long list of benefits, from calming nerves to reducing inflammation in joints. But how can one supplement have so many different effects?
The key to understanding how CBD works is a part of the body called the endocannabinoid system. More specifically:
- What the endocannabinoid system is, and
- How CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system (often shortened to the ECS) reaches across all major organs, including the brain, the nervous system, and the skin. Its purpose is to help the body regulate its responses to stress and stimuli.
The main receptors in the ECS are called cannabinoid receptors, which are activated by molecules called cannabinoids. There are multiple types of cannabinoids, each of which transmits information related to the release of hormones and enzymes, and the activation of inflammation.
Researchers believe that the ECS is partly responsible for many bodily processes, including inflammation, sleep, pain, and immune response.
When was the endocannabinoid system discovered?
In the 1980s, scientists studying the brain discovered the existence of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors.
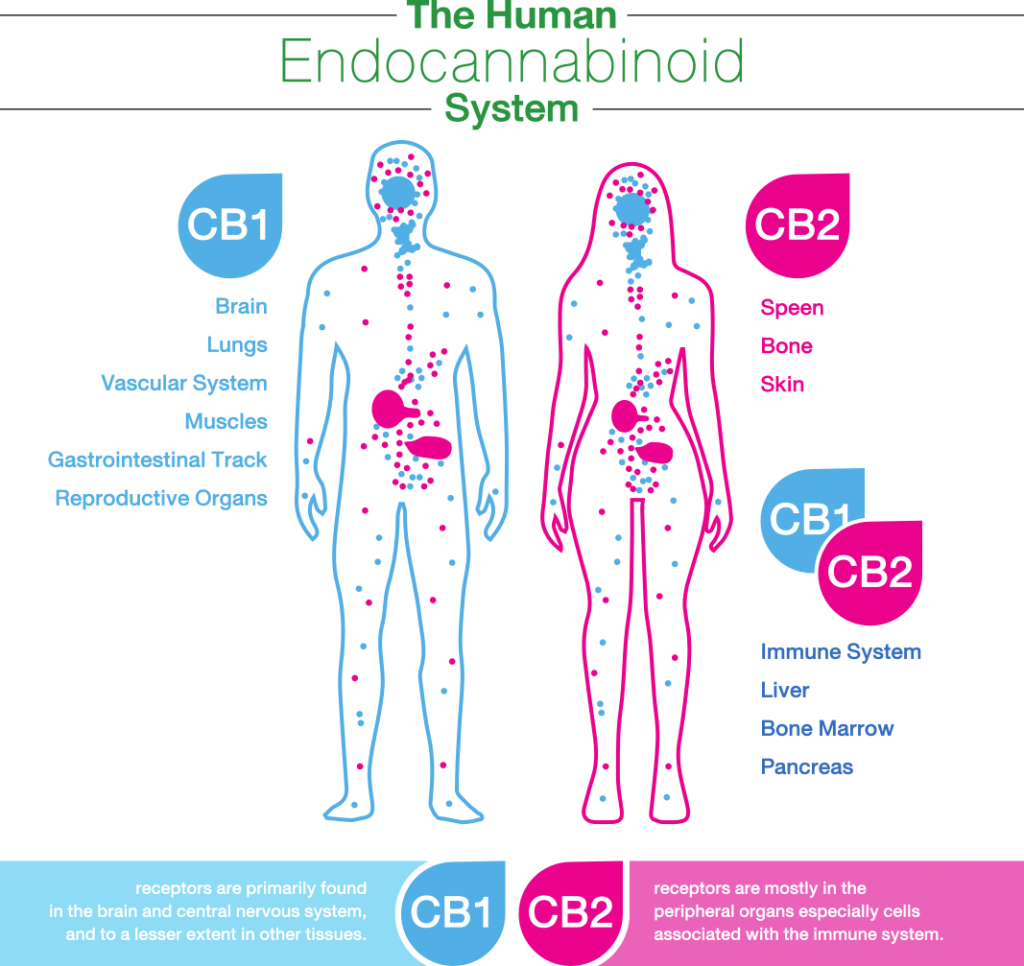
A couple of years later, researchers looking more deeply at cannabinoid receptors found that they could be classified into two main types—CB1 and CB2—and that CB2 receptors exist throughout the immune system, nervous system, and other major organs.
This lead to the full discovery of the endocannabinoid system in 1992. Dr. Allyn Howlett and Dr. William Devane are credited with identifying the first cannabinoid, which they nicknamed anandamide after a Sanskrit word meaning bliss, thanks to its role in reducing pain.
Today, scientists believe that there are two main cannabinoids produced by the body, anandamide and 2-archidonyl glycerol (2-AG), which are technically known as endocannabinoids.
Despite being such a late discovery, scientists now understand that all mammals and most vertebrate species have an endocannabinoid system.
What does the endocannabinoid system do?
The endocannabinoid system is involved in regulating many essential bodily systems, including the triggering of anxiety, pain, and inflammation.
The ECS also plays a role in mood-regulation, motor control, sleep cycles, and temperature control.
By modulating these functions, the ECS helps us maintain internal balance inside the body, known in medical literature as homeostasis.
Homeostasis is the process by which organisms can keep functioning steadily (heartbeat, temperature, mental state, etc.) despite environmental conditions constantly changing around them.
The endocannabinoid system and CBD
The full name for cannabinoids made naturally by the body is called endocannabinoids. But there’s another category of compounds that are also able to stimulate the endocannabinoid system.
Known as phytocannabinoids, these compounds have been identified in several plants, with cannabis being thought to contain over 100 of them.
CBD is one of the most common phytocannabinoids, along with THC. Others include CBG, CBN, CBC, and CBD-A, each of which interacts slightly differently with the endocannabinoid system to produce different effects.
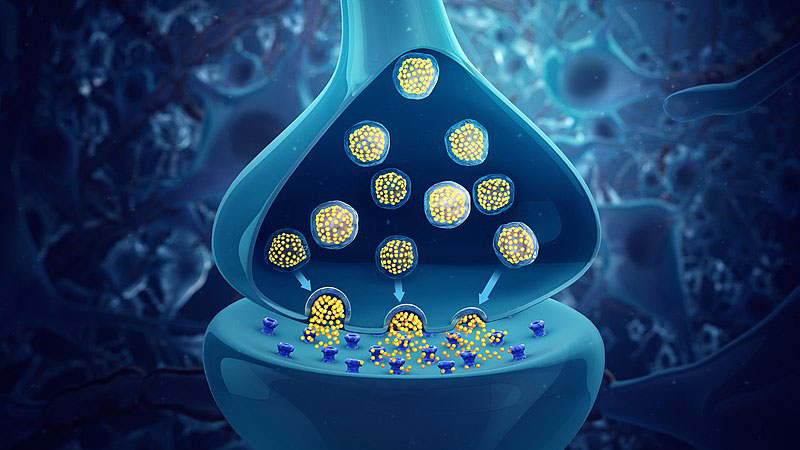
How do cannabis compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system?
Cannabinoids are a little bit like keys, able to unlock and activate certain receptors in the endocannabinoid system.
For example, THC and CBN act in a lock-and-key fashion with CB1 receptors in the brain and nervous system–which partly helps to explain why these two cannabinoids are known to produce psychoactive effects.
CBN, on the other hand, seems to prefer the CB2 receptors in the immune system.
Did you know: The body’s enzymes are less effective at breaking down phytocannabinoids than endocannabinoids. This is one of the main reasons why cannabis is able to have a long-lasting effect on inflammation.
How does CBD interact with the endocannabinoid system?
Unlike other cannabinoids, CBD doesn’t usually bind directly receptors in a lock-and-key manner.
Instead, CBD modulates endocannabinoid receptors to affect how other cannabinoids bind with them. For example, CBD inhibits the action of THC, which is thought to soften some of that compound’s more intense effects.
As a result of the way it interacts with receptors, CBD can also help the body to maintain cannabinoids. CBD uses up enzymes that are normally involved in breaking down other compounds.
CBD’s anti-anxiety effects can be traced to its ability to help the body conserve the cannabinoid anandamide, keeping enzymes from metabolizing it. This is somewhat comparable to how SSRI anti-anxiety medication functions.
Other Ways CBD Affects the Body
Besides interacting with CB receptors CBD affects a host of additional receptors in the body, including:
Dopamine
Receptors:
CBD binds to Dopamine D2 receptors, which are involved in the treatment of schizophrenia.
TRP
Receptors:
CBD and other phytocannabinoids activate TRP1 receptors, which may contribute to their analgesic effects.
PPAR Gamma
Receptors:
CBD activates PPAR receptors, which are involved in conditions like diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
5-ht1A
Receptors:
CBD stimulates 5-ht1A receptors, which play a role in a variety of vital systems.
The entourage effect
The entourage effect describes something that both cannabis users and researchers have noticed: CBD oils that contain lots of different cannabinoids often have a stronger and more well-rounded effect than those containing only isolated CBD. This isn’t just because there are more cannabinoids; taking them together actually seems to increase the effectiveness of each cannabinoid compared to their strength when supplied individually.
CBD oils that contain a range of cannabinoids, including traces of THC, are called full-spectrum. You can find the different cannabinoids, like CBD, THC, CBC, CBN, CBG & more in the full spectrum CBD oil lab report.
Endocannabinoid system diagram
Here’s a simple visual illustration of the endocannabinoid system:
CBD and animals
All vertebrate organisms have an endocannabinoid system, including mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish. Even some invertebrates, such as mussels, leeches, and sea urchins, have endocannabinoid systems.
CBD has a similar effect on mammals as it does on humans. Because of this pet-owners are increasingly turning to CBD oil for their dogs and cats to help with common inflammatory problems such as anxiety and arthritis.
Did you know: insects lack an endocannabinoid system, which is why cannabis doesn’t seem to affect bees and other creepy crawlies that pollinate cannabis flowers.
Summary
By interacting with the endocannabinoid system, CBD is able to create a range of soothing effects on the body—and even dogs are able to experience CBD’s benefits.
Here are some keywords associated with CBD and the endocannabinoid system:
-
The ECS
An abbreviation for the endocannabinoid system, a regulating function within the body that responds to cannabis compounds.
-
CB1 & CB2 receptors
These are the two main categories of receptors found within the endocannabinoid system. Both are activated by cannabinoids.
-
Cannabinoid
Signaling molecules that interact with CB receptors in the endocannabinoid system.
-
Endocannabinoids
The full name for cannabinoids created naturally within the body.
-
Phytocannabinoids
The full name for cannabinoids found within cannabis and some other plants.
-
Cannabidiol
The full name for CBD, one of the main phytocannabinoids found in cannabis.
-
THC
The cannabinoid found in cannabis that’s associated with intoxication, psychoactive effects, appetite stimulation, and pain relief. Its full name is Tetrahydrocannabinol.
-
Homeostasis
The term for internal bodily balance.
-
Endogenous
The term for compounds that are created naturally by the body
-
Endocannabinoids are endogenous compounds.
